

(Organic_Chemistry)/Amides/Properties_of_Amides/Physical_Properties_of_Carboxylic_Acid_Derivatives Carboxylic Acids and its Derivatives Authors: Hisham Essam Hasan Zarqa University Abstract Carboxylic acids are present in many industrial processes and most biological pathways and are.Pop-up menu will appear, select Chemistry from the given list. Bring the arrow towards NEET which can be seen in the navigation bar. WebCandidates preparing for the chapter Carboxylic Acids & Their Derivatives can go through the NEET Chemistry notes. This method leads to the so far … fhm trainex 24 bielefeldĬhapter 12 Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives - Soka Carboxylic acid and derivatives pdfĬarboxylic Acids and Derivatives Nomenclature – Examples Organic Chemistry - Problem Drill 15: Carboxylic Acids and …
The use of mild conditions of deprotection of the BOC group, which does not result to the cleavage of the cage-like silsesquioxane structure, is reported.
#Reactivity of carboxylic acid derivatives mcat pdf#
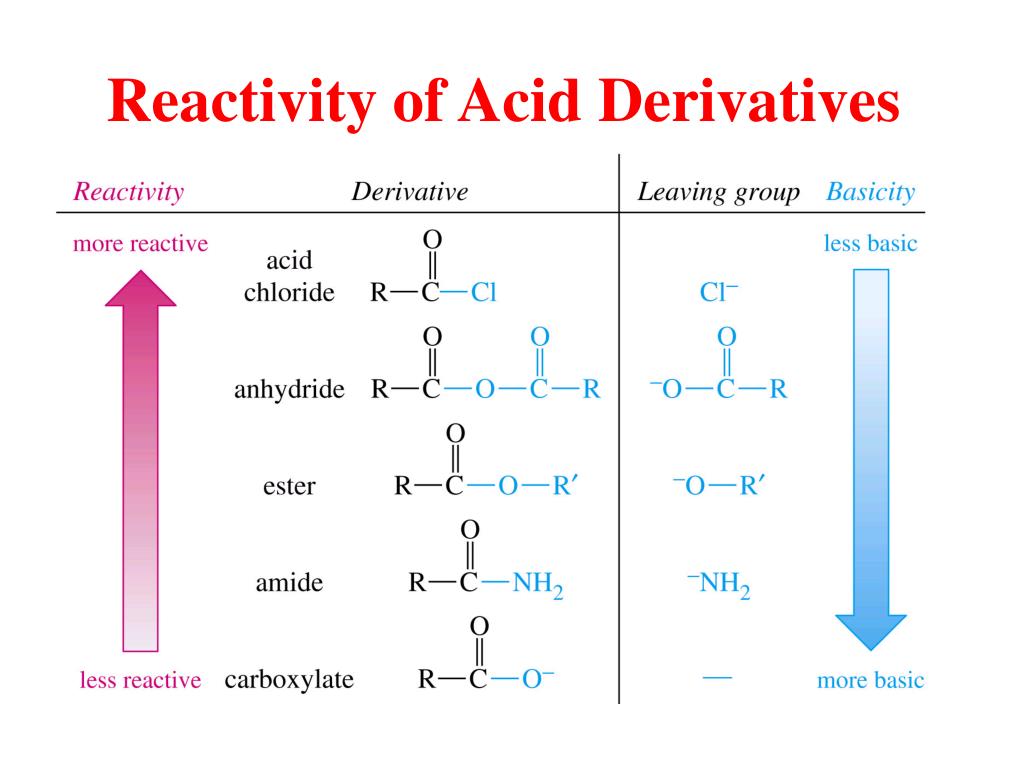
(PDF) Catalytic Oxidative Decarboxylation of Some … Ĭarboxylic acids and derivatives Organic chemistryġ8.7: Reduction of Carboxylic Acids and Their DerivativesĬarboxylic Acid and Derivatives PDF Ester Carboxylic Acid Carboxylic acid and derivatives pdf We will see how this works in the next section.(Organic_Chemistry)/Carboxylic_Acids/Properties_of_Carboxylic_Acids/Carboxyl_Derivatives/Carboxylic_Derivatives_-_Reduction_(Catalytic_Reduction) To go 'uphill' - from a carboxylate to a thioester, for example, requires the 'coupling' of the uphill reaction to an energetically favorable reaction. Thioesters, for example, are often converted directly into carboxylic esters in biochemical reactions, but not the other way around. In general, acyl substitution reactions convert higher energy carboxylic acid derivatives into derivatives of lower energy. In general, if the incoming nucleophile is a weaker base than the ‘acyl X’ group that is already there, it will also be the better leaving group, and thus the first nucleophilic step will simply reverse itself and we’ll get the starting materials back: Recall from chapter 7 that the \(pK_a\) of a thiol is about 10, while the \(pK_a\) of an alcohol is 15 or higher: a stronger conjugate acid means a weaker conjugate base. A thioester is more reactive than an ester, for example, because a thiolate (RS-) is a weaker base and better leaving group than an alcoxide (\(RO\)-). The reactivity trend of the carboxylic acid derivatives can be understood by evaluating the basicity of the leaving group (acyl X group) - remember from section 8.4 that weaker bases are better leaving groups. Relative reactivity of carboxylic acid derivatives: Section 11.8 near the end of this chapters includes information about the chemistry of these two reagents. Acid anhydrides and acid chlorides are laboratory reagents that are analogous to thioesters and acyl phosphates, in the sense that they too are highly reactive carboxylic acid derivatives. In carboxylic acid derivatives, the partial positive charge on the carbonyl carbon is stabilized by electron donation from nonbonding electrons on the adjacent heteroatom, which has the effect of decreasing electrophilicity.Īmong the carboxylic acid derivatives, carboxylate groups are the least reactive towards nucleophilic acyl substitution, followed by amides, then carboxylic esters and carboxylic acids, thioesters, and finally acyl phosphates, which are the most reactive among the biologically relevant acyl groups.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
